24-Apr-2025

Choosing the Perfect Water Softener for Your Home: Types, How They Work, and Costs.
Hard water can be a constant challenge in your home, causing issues like soap scum in showers and limescale buildup in pipes. These mineral deposits don't just create cleaning headaches—they can damage your plumbing system and appliances over time, potentially leading to costly repairs.
Water softener systems offer an effective solution to these problems, with benefits extending beyond your pipes to improvements for your skin and hair. This guide explores how these systems function, the options available, and the key factors to consider when selecting the right water softener for your household needs.
Understanding Hard Water
Hard water contains high levels of dissolved minerals, primarily calcium and magnesium. These minerals naturally accumulate in groundwater through limestone, dolomite, and similar rock formations. Hard water’s calcium and magnesium are generally safe and contribute to dietary minerals. Still, excessive levels may cause minor digestive discomfort in sensitive individuals or increase kidney stone risk for those predisposed. They also lead to pipe scaling and reduced soap efficiency.
Water hardness is typically quantified using two equivalent measurements:
Water exceeding 120 PPM is officially considered hard water. You might recognize this condition through common signs like water spots on clean dishes or a persistent film left on your skin after bathing.
The Hidden Costs of Hard Water
Shortened Appliance Lifespan: Scale accumulation forces water heaters, washing machines, and dishwashers to operate less efficiently, leading to premature failures.


Destructive Mineral Deposits: The whitish buildup visible on fixtures isn't merely unsightly—it progressively restricts water flow and damages pipe materials over time.

Personal Care Challenges: Hard water prevents proper soap lathering, resulting in residue that can leave skin feeling dry and hair looking lacklustre.

Increased Utility Expenses: As scale-affected appliances struggle to function properly, they consume significantly more energy, causing noticeable increases in your monthly utility costs.

The Secret Weapon Against Hard Water: What’s Inside Your Water Softener?
1. Mineral Tank (Resin Chamber)
2. Brine Tank
3. Control Valve (Head Unit)
Function: The "brain" of the system, automating cycles and monitoring water usage.
Key Features:
Timer or Metered Control: Determines when to initiate regeneration based on time (e.g., nightly) or actual water usage.
Cycle Settings: Manages the backwash, brine draw, slow rinse, and fast rinse phases of regeneration.
Bypass Valve: Allows you to temporarily shut off soft water flow for maintenance.
Manual Override Option: Some models offer manual regeneration settings, allowing users to trigger regeneration when needed without waiting for the automated cycle.
Why It Matters: Ensures the system regenerates efficiently with or without automation, giving users more control when required.
A manually operated valve used to regulate, redirect, or shut off fluid flow (water, gas, oil, etc.) in pipelines or systems. Unlike automated valves, it requires physical adjustment via handles, wheels, or levers.
Operation: Adjusted by hand (e.g., turning a wheel, pulling a lever).
Types: Includes ball valves, gate valves, globe valves, butterfly valves, and multiport valves.
No External Power: Relies on human input—ideal for simple systems or emergencies.
Durability: Fewer moving parts = lower failure risk.
4. Drain Line
5. Resin Beads
The Softening Cycle Explained
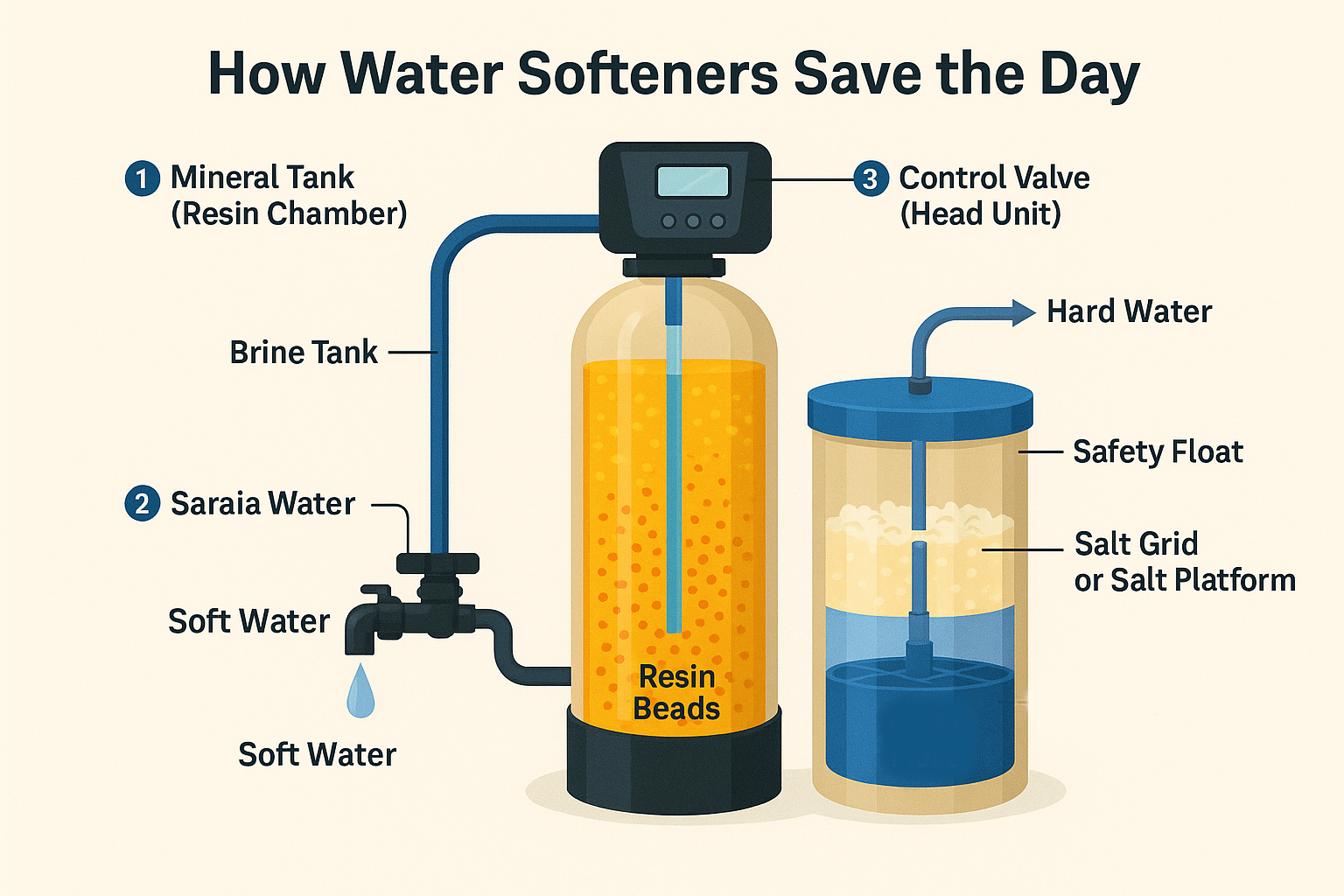
This continuous regeneration process ensures your water softener maintains optimal performance, delivering consistently soft water throughout your home's plumbing system
When selecting a water softener, your specific circumstances will determine which technology best addresses your home's unique water challenges. Here's an in-depth look at the available options:
Traditional Salt-Based Ion Exchange Systems

Ideal Application: Households battling severe water hardness (exceeding 200 PPM) where maximum mineral removal is essential.
Technology Explained: These systems employ the classic ion exchange method, using charged resin beads to capture hardness minerals and release sodium ions in their place.
Advantages:
Considerations:
Salt-Free Water Conditioning Systems

Ideal Application: Homes with mild to moderate hardness seeking scale prevention without introducing sodium; environmentally conscious households.
Technology Explained: Using Template Assisted Crystallization (TAC) media, these systems transform dissolved minerals into microscopic crystals that remain suspended in water rather than adhering to surfaces.
Advantages:
Considerations:
Continuous Service Dual-Tank Systems

Ideal Application: Large households with high water consumption or settings where uninterrupted soft water access is crucial.
Technology Explained: Features two alternating resin tanks that provide seamless operation—while one tank regenerates, the other supplies softened water.
Advantages:
Considerations:
Electronic and Magnetic Descaling Solutions

Ideal Application: Rental properties or situations where plumbing modifications are restricted; mild hardness cases.
Technology Explained: These devices create electromagnetic fields that alter the behavior of minerals, theoretically reducing their tendency to form scale deposits.
Advantages:
Considerations:
Compact Portable Softening Units


Ideal Application: RVs, boats, small apartments, or temporary living situations.
Technology Explained: Miniaturized versions of traditional salt-based systems, designed for limited space and lower water volumes.
Advantages:
Considerations:
When evaluating these options, consider your water hardness level, household size, budget constraints, and specific concerns (scale prevention, skin sensitivity, or appliance protection) to determine which technology offers the optimal solution for your situation.
Now that we’ve explored water softener options, let’s focus on Pearl Water Technologie’s advanced solutions. We combine innovation with reliability to tackle hard water challenges—delivering smarter, simpler results for homes and businesses. Discover how we’re redefining water softening.
Types of Water Softeners by Pearl Water Technologies
Fully Automatic Water Softener

Semi-Automatic Water Softener

Domestic Water Softener (for Home & Bathroom)

Industrial Water Softener

Commercial Water Softener Plant

Portable Water Softener

Installation: DIY or Call a Pro?
Keeping Your System Happy: Maintenance Tips
Cost Breakdown in India (2025)
Prices vary by brand (e.g.,Pearl Water Technologies), capacity, and installation complexity.
Health & Environmental Notes
Alternatives to Whole-House Softening
Final Thoughts
A water softener isn’t just a luxury—it’s a long-term investment in your home’s health. By easing appliance strain, cutting energy bills, and sparing you from endless scrubbing, the right system pays for itself over time. Start by testing your water hardness (many companies offer free tests!), then weigh your budget and household needs. With proper care, your softener will keep your water—and your life—flowing smoothly for years to come.
Ready to say goodbye to hard water? Share your questions or experiences in the comments below!
FAQ:-
1. What is a water softener?
A water softener removes hard minerals like calcium and magnesium from water to prevent scale buildup.
2. Why should I install a water softener at home?
It protects your pipes, extends appliance life, and makes water better for skin, hair, and cleaning.
3. How do I know if I have hard water?
If you see white spots on taps, dull laundry, or dry skin, you likely have hard water.
4. Is a water softener easy to install?
Yes, most water softeners are easy to install with basic plumbing tools or with a plumber’s help.
5. How often should I refill the salt in a water softener?
Usually, once a month, depending on your water usage and the model.
6. Does soft water help skin and hair?
Yes, soft water feels gentle, reduces dryness, and improves hair texture.
7. Do smart water softeners work with mobile apps?
Yes, many smart models can be controlled and monitored through mobile apps.
Leave A Comment